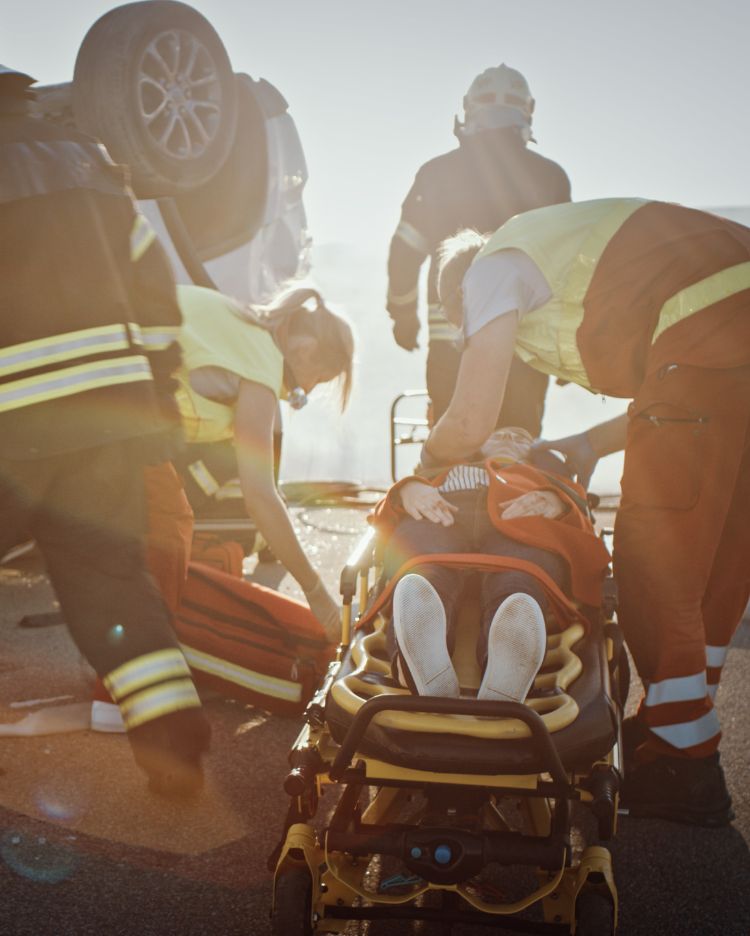
Car accident compensation offers a pathway to rebuilding what negligence has destroyed. Under Ontario law, victims can pursue comprehensive damages that address not only immediate costs but also the profound ways serious injuries reshape lives. The compensation process recognizes that a severe accident doesn’t simply generate medical bills—it can eliminate your ability to work, strain family relationships, and rob you of activities that once brought joy and meaning.
Working with a Hamilton car accident lawyer is essential when navigating this complex legal landscape. Understanding your rights, methodically building evidence, and pursuing every available avenue for recovery are all critical steps. For families facing the overwhelming aftermath of a serious collision, securing appropriate compensation becomes vital—not only to cover expenses but also to reclaim stability and hope for the future.
Get Your Free Legal Consultation Today
Contact Us Today
Common Causes of Car Accidents in Hamilton, Ontario
Hamilton’s collision statistics reveal patterns that continue endangering families throughout the region. The leading causes stem from dangerous driving behaviours that transform routine trips into life-altering tragedies.
Head-On Collisions
Head-on crashes occur when vehicles cross into oncoming traffic lanes, creating devastating impacts from combined speeds. These accidents frequently result from unsafe passing attempts, drowsy driving, and impaired operation. The tremendous forces involved make head-on collisions among the most catastrophic accident types, often causing traumatic brain injuries, spinal cord damage, and multiple organ trauma.
Our firm has represented numerous clients whose lives were forever altered by head-on collisions, many of whom require extensive rehabilitation and lifelong care. The physics of these crashes—where closing speeds can exceed 120 km/h—generate impact forces that overwhelm even modern safety systems. We frequently see complex injury patterns including spinal cord injury, cervical spine fractures, severe facial trauma, and internal bleeding that require immediate surgical intervention. The financial implications extend far beyond initial emergency treatment, as clients often face years of specialized therapy, adaptive equipment needs, and permanent disability accommodations that can total millions of dollars over a lifetime.
T-Bone or Side-Impact Collisions
Hamilton data shows 55% of all collisions occurred at intersections, with 37% of fatal accidents happening at these locations. T-bone accidents happen when one vehicle’s front end strikes another vehicle’s side, typically during red light violations, failure to yield right-of-way, and distracted driving incidents. The limited side protection in most vehicles makes occupants particularly vulnerable to serious injuries.
These intersection collisions present unique legal challenges, as establishing fault often requires detailed accident reconstruction and analysis of traffic signal timing, sight lines, and witness testimony. Our experience handling T-bone cases has shown that occupants on the struck side frequently suffer from traumatic brain injuries due to lateral acceleration forces, along with pelvic fractures, rib injuries, and internal organ damage. The medical complexity of these cases demands thorough documentation of both immediate trauma and long-term complications such as post-concussion syndrome, chronic pain conditions, and psychological trauma. Insurance companies often underestimate the full scope of damages in side-impact collisions, making experienced legal representation essential for securing appropriate compensation.
Roll-Over Collisions
Rollover accidents involve vehicles flipping onto their side or roof, often affecting SUVs, trucks, and high-profile vehicles during sharp turns or overcorrection attempts. These crashes frequently occur when vehicles strike objects like curbs, guardrails, or soft shoulders. The lack of structural protection during rollovers exposes occupants to ejection, crushing injuries, and multiple trauma.
The chaotic nature of rollover accidents creates particularly severe injury patterns that our legal team has extensively documented through expert testimony and medical evidence. Beyond the immediate trauma of roof crush injuries and ejection-related wounds, survivors often endure complex orthopedic injuries requiring multiple surgeries, prolonged rehabilitation, and permanent mobility limitations. Vehicle defect claims may arise when roof strength proves inadequate or safety restraint systems fail during the rollover sequence. Our firm conducts thorough investigations into vehicle maintenance records, tire condition, and roadway design factors that may have contributed to the rollover, as these elements can significantly impact liability determination and compensation recovery.
Pedestrian Collisions
Nine pedestrians died in seven fatal crashes in Hamilton during 2022. Pedestrian accidents occur at crosswalks, in parking lots, and on residential streets when drivers fail to yield, operate while distracted, or don’t account for poor visibility conditions. The vulnerability of pedestrians means even low-speed collisions can cause life-threatening injuries.
Our pedestrian accident cases reveal the devastating disparity between human vulnerability and vehicle mass, where even minor impacts can result in catastrophic injuries requiring immediate trauma response. We regularly advocate for clients suffering from lower extremity fractures, pelvic injuries, and head trauma that fundamentally alter their mobility and independence. The legal complexity increases when examining municipal liability for inadequate crosswalk design, insufficient lighting, or poorly maintained sidewalks that contribute to accident risk. Insurance adjusters often attempt to assign contributory negligence to pedestrians, making it crucial to preserve physical evidence, obtain surveillance footage, and secure expert accident reconstruction analysis that accurately depicts the collision dynamics and driver responsibilities under Ontario’s Highway Traffic Act.
Bicycle Accidents
Bicycle accidents happen when drivers fail to provide adequate space, don’t check blind spots, or open vehicle doors into cyclists’ paths. The increasing popularity of cycling for transportation and recreation has created more interaction between bicycles and motor vehicles, often resulting in serious injuries due to the size and weight differences between vehicles and bicycles.
The surge in cycling infrastructure throughout Hamilton has unfortunately not eliminated the serious risks cyclists face when sharing roadways with motor vehicles. Our cycling accident practice has documented patterns of severe injuries including clavicle fractures, road rash requiring skin grafts, and traumatic brain injuries that occur despite helmet use. “Dooring” incidents present particular legal challenges, as they involve both driver negligence and municipal road design considerations that affect cyclist safety zones. We work closely with cycling safety experts and biomechanical engineers to demonstrate how driver inattention, inadequate shoulder width, or poorly designed bike lanes contribute to collision risk. The economic impact extends beyond medical treatment to include specialized bicycle equipment, modified vehicles for transportation during recovery, and often significant time away from employment for clients whose work requires physical capability or bicycle commuting.
Common Injuries in Car Accidents in Hamilton, Ontario
Car accident injuries can permanently alter victims’ physical capabilities, cognitive function, and quality of life. Understanding these injury types helps families prepare for the extensive recovery process and compensation they may require.
Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury
Spinal cord injuries: SCI’s range from incomplete damage causing partial paralysis to complete severing resulting in quadriplegia or paraplegia. These injuries affect sensation, movement, and bodily functions below the injury site. Recovery requires extensive rehabilitation, home modifications for wheelchair accessibility, specialized medical equipment, and lifetime attendant care.
The financial impact includes immediate medical costs, ongoing therapy expenses, equipment replacement, and significant modifications to housing and transportation. Many spinal cord injury victims require 24-hour care assistance for basic daily activities, creating substantial ongoing costs that can exceed millions of dollars over a lifetime.
Our spinal cord injury practice has revealed the inadequacy of initial medical assessments in predicting long-term care requirements and associated costs. Beyond the obvious paralysis, clients frequently develop secondary complications including autonomic dysreflexia, pressure sores, respiratory complications, and urinary tract infections that require specialized medical intervention throughout their lives. The psychological adjustment to spinal cord injury often necessitates ongoing counseling and psychiatric care, while family members may require respite services and their own therapeutic support. Insurance companies routinely underestimate these comprehensive care needs, particularly the costs associated with attendant care inflation, equipment replacement cycles, and the increased medical complications that emerge with aging. Our legal team works with life care planners, rehabilitation engineers, and vocational experts to document the full spectrum of lifetime costs, ensuring that settlements or court awards provide genuine security rather than merely covering immediate expenses.
Traumatic Brain Injury
Brain injuries affect cognitive function, memory, personality, emotional regulation, and motor skills. Even mild traumatic brain injuries can cause lasting effects on work capacity, relationships, and daily functioning. Severe brain injuries may require lifetime supervision and care.
Recovery often involves neuropsychologists, speech therapists, occupational therapists, and cognitive rehabilitation specialists. The hidden nature of many brain injury symptoms can make these cases particularly challenging to document and pursue, requiring comprehensive neuropsychological testing and expert medical opinions.
Fractures in Weight-Bearing Joints
Fractures to elbows, wrists, knees, and hips significantly impact mobility and independence. Complex fractures often require multiple surgeries, extended rehabilitation, and may result in permanent arthritis, chronic pain, and limited range of motion. Weight-bearing joint injuries affect walking, climbing stairs, lifting, and other essential activities.
Recovery may require joint replacement surgeries, ongoing physiotherapy, pain management, and adaptive equipment. The long-term consequences can include early retirement, career changes, and reduced participation in recreational activities that previously provided enjoyment and social connection.
Beyond the immediate surgical interventions and rehabilitation protocols, these injuries frequently lead to compensatory movement patterns that accelerate wear in adjacent joints, creating a progressive cycle of deterioration requiring additional medical intervention. Our orthopedic cases often involve expert testimony regarding the inevitability of future joint replacements, the limited lifespan of prosthetic devices, and the increasing surgical risks associated with revision procedures as clients age. The vocational impact extends beyond obvious physical limitations to include reduced stamina, chronic pain management requirements, and weather sensitivity that affects work attendance and productivity. We work closely with occupational therapists and ergonomic specialists to quantify how joint limitations affect specific job functions, while life care planners project the costs of future surgical procedures, ongoing pain management, and adaptive technologies that enable continued independence. Insurance companies frequently minimize these injuries as routine orthopedic problems, failing to recognize how weight-bearing joint damage fundamentally alters a person’s relationship with physical activity, recreational pursuits, and basic mobility throughout their remaining lifetime.
Car Accident Compensation in Canada
Canada’s legal system provides several categories of compensation designed to address the full scope of losses experienced by accident victims and their families.
Non-Economic Damages
Pain and Suffering Compensation: compensate for intangible losses that cannot be calculated through receipts or financial records but represent real and significant harm to accident victims. The law recognizes that the effects of a severe accident can touch every aspect of life, often bringing feelings of loss, fear, and uncertainty about the future, and courts consider each case’s unique circumstances and strive to reach a fair outcome.
Pain and suffering compensation addresses physical pain, emotional distress, anxiety, depression, and psychological trauma resulting from injuries, including ongoing pain, sleep disturbances, anxiety about future health, depression from lifestyle limitations, and the psychological impact of permanent disability.
Loss of enjoyment of life damages recognize that injuries prevent participation in activities, hobbies, sports, travel, and experiences that previously brought meaning and satisfaction, while loss of amenities addresses practical limitations such as inability to drive, reduced mobility, dependence on others for basic care, and loss of independence in daily activities.
In Canada, the Supreme Court established a cap on general damages in 1978 at $100,000, which is adjusted annually for inflation and currently sits at approximately $469,801 as of August 2025. This cap applies only to compensation for pain and suffering, not to other forms of damages such as the cost of future care or lost income, which often make up a large portion of the total award in serious injury cases.
Courts assess general damages by considering the severity of injuries, the impact on daily life, recovery period, age of the plaintiff, emotional and psychological impact, pre-existing conditions, and comparable cases to ensure consistency.
The compensation awarded will depend on the severity and circumstances of your injury, with more severe and life-altering injuries resulting in higher awards, though the maximum is reserved for the most catastrophic cases involving quadriplegia, serious traumatic brain injuries, and other devastating injuries.
Compensation for Family Members: Ontario’s Family Law Act recognizes that serious injuries affect entire families, not just the injured person. Close family members can pursue compensation for their own losses resulting from their loved one’s injuries or death . Eligible family members include spouses, children, parents, grandparents, and siblings.
Family Law Act claims can include:
- Actual expenses incurred for the injured person’s benefit
- Loss of income from providing care to the injured family member
- Travel expenses for hospital visits during treatment and recovery
- Compensation for loss of guidance, care, and companionship
- Mental distress suffered by family members witnessing traumatic circumstances
Recent cases have awarded $250,000 to each parent for loss of care, guidance, and companionship, representing a significant increase from previous awards of approximately $100,000. These higher awards recognize the profound impact serious injuries have on family relationships and dynamics.
Economic Damages
Economic damages compensate for quantifiable financial losses directly caused by accident injuries. These damages often represent the largest portion of personal injury settlements and court awards.
Past Income Loss: Past income loss addresses employment income lost from the accident date until trial or settlement. This calculation encompasses base salary, overtime pay, bonuses, commission, benefits, pension contributions, and other employment-related compensation.
For self-employed individuals, past income loss analysis requires examining business records, contracts, projected income, and lost business opportunities. Professional economic analysis helps quantify these complex calculations and present compelling evidence to insurance companies and courts.
Future Wage Loss or Loss of Earning Capacity: Future income loss compensation addresses the harsh reality that serious injuries can permanently diminish your earning capacity throughout your remaining working life, potentially costing hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars over time. Courts assess this damage by examining your pre-accident career trajectory, education level, skills, work experience, age, and the specific functional limitations your injuries now impose, then calculate what you would have reasonably earned versus what you can now earn given your medical restrictions and reduced capabilities.
The assessment examines whether the person can return to their previous occupation, requires career changes, must work reduced hours, or faces early retirement due to injury-related limitations. Expert vocational assessment and economic analysis help quantify these losses over the injured person’s expected working lifespan.
Factors affecting future income loss include:
- Ability to perform physical job requirements
- Cognitive capacity for complex tasks
- Stamina for full-time employment
- Career advancement opportunities
- Retraining requirements for alternative employment
Loss of Housekeeping Capacity: The loss of housekeeping recognizes that injuries can eliminate or reduce the ability to perform household tasks previously managed independently. This includes cleaning, cooking, home maintenance, yard work, childcare responsibilities, and other domestic activities.
The compensation acknowledges that losing the capacity to care for one’s home represents a real loss, regardless of whether family members provide assistance or outside help is hired. Courts recognize the value of this capacity even when alternative arrangements address the practical needs.
Future Care Costs Not Covered by OHIP or Accident Benefits: While Ontario provides healthcare coverage through OHIP and accident benefits through auto insurance, significant care needs often exceed these systems’ limitations. Future care costs can include private nursing care, specialized therapies, equipment replacement, home modifications, and experimental treatments.
Professional life care planners, typically occupational therapists with specialized training, assess future needs and quantify associated costs. These assessments consider:
- Medical equipment needs throughout the person’s lifetime
- Home accessibility modifications
- Vehicle adaptations for transportation
- Specialized therapy requirements
- Attendant care for daily activities
- Equipment maintenance and replacement schedules
Dependency Claims: A dependency claim in Ontario is brought under the Family Law Act by surviving family members (including spouses, children, parents, grandparents, and siblings) when a person dies as a result of someone else’s negligence, allowing them to recover compensation for the financial support they lost due to the death. These claims involve both pecuniary damages (measurable financial losses like lost income, pension benefits, and household services) which are calculated using forensic accounting reports based on the deceased’s expected lifespan and working capacity, and non-pecuniary damages for loss of guidance, care, and companionship.
Understanding Ontario’s Accident Benefits System
Ontario’s Statutory Accident Benefits Schedule (SABS) creates a three-tier system determining available compensation based on injury severity. Understanding these categories helps families know what resources are available through their auto insurance policy.
Minor Injury Guideline (MIG)
The Minor Injury Guideline covers strains, sprains, whiplash, and minor soft tissue injuries. Individuals classified under MIG receive up to $3,500 for medical and rehabilitation benefits. This category applies to injuries expected to recover within a few months with standard treatment.
Non-Catastrophic Injuries
Non-catastrophic impairment under Ontario’s Statutory Accident Benefits Schedule (SABS) applies to injuries that are more severe than minor injuries but do not meet the definition of catastrophic impairment, such as fractures and other significant injuries that fall outside the Minor Injury Guideline. For accidents occurring on or after June 1, 2016, individuals with non-catastrophic injuries are entitled to a combined maximum of $65,000 for medical, rehabilitation, and attendant care benefits, payable for up to 5 years following the accident at a maximum rate of $3,000 per month.
Catastrophic Impairment
Catastrophic impairment under Ontario’s Statutory Accident Benefits Schedule (SABS) is a designation for the most severe motor vehicle accident injuries that significantly increases available benefits from $65,000 to $1 million for medical and rehabilitation costs. To qualify, an injured person must meet specific medical criteria including severe traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury resulting in paraplegia or quadriplegia, amputation of limbs, severe impairment of mental or physical function, or a combination of injuries that substantially impairs multiple body systems. This designation must be determined through medical assessments and provides access to enhanced attendant care benefits, housekeeping allowances, and other support services, recognizing that these individuals require long-term, intensive care and rehabilitation.
In Ontario, purchasing the optional catastrophic impairment benefit provides an additional $1 million in coverage for medical, rehabilitation, and attendant care, bringing the total potential benefit for a catastrophically injured person to $3 million. This is on top of the standard $1 million that catastrophic injuries are entitled to, plus the optional $1 million for non-catastrophic injuries that some policyholders also purchase.
Am I Catastrophically Impaired?
If you sustained injuries in an accident on or after June 1, 2016, you qualify for catastrophic benefits when your injuries meet specific criteria. The insurance system recognizes eight main categories of catastrophic impairment, and you need to meet the requirements of only one category to qualify.
1. Spinal Cord Injuries (Paraplegia or Tetraplegia)
You qualify if you have paralysis affecting your legs (paraplegia) or all four limbs (tetraplegia) and medical professionals can determine your permanent neurological status. Your condition must meet specific medical standards showing severe permanent impairment. This includes cases where you score very low on mobility tests (0 to 5 points when walking up to 10 meters indoors), require catheterization or surgical procedures to manage bladder function, or need special routines or devices to manage bowel function.
2. Severe Loss of Mobility or Limb Function
You qualify if you have lost a leg through amputation at or above the shin level, have lost an arm or completely lost the use of an arm, or have severe permanent damage to one or both legs that leaves you unable to walk indoors without significant assistance (scoring 0 to 5 on standard mobility tests).
3. Vision Loss in Both Eyes
You qualify when you have lost vision in both eyes to the point where, even with glasses or medication, your visual sharpness measures 20/200 or worse on standard eye charts, or your field of vision narrows to 20 degrees or less. Medical professionals must confirm that physical causes, not psychological factors, create this vision loss.
4. Traumatic Brain Injury (Adults 18 and Over)
You qualify if you were 18 or older at the accident and suffered a brain injury that shows clear damage on brain scans (CT, MRI, or other recognized technology). The scans must reveal physical brain damage such as bleeding, swelling, or tissue damage from the accident. Additionally, standardized assessments must show that you remain in a vegetative state for at least one month, have severe disability for at least six months, or have moderate disability that persists for at least one year after the accident.
5. Traumatic Brain Injury (Children Under 18)
Children under 18 qualify through several pathways. The child qualifies when a public hospital admits them as an inpatient with brain scans showing accident-related damage, or when a pediatric rehabilitation facility accepts them into a neurological rehabilitation program. The child also qualifies if standardized pediatric assessments show they remain in a vegetative state for at least one month, have severe disability for at least six months, or need supervision or help for most of their waking hours nine months after the accident due to serious physical, thinking, or behavioral problems.
6. Physical Impairments Totaling 55% or More
You qualify when physical injuries result in 55% or more whole-body impairment according to the American Medical Association’s guides (4th edition). However, you must wait two years after the accident to apply under this category, unless a physician assesses you three months post-accident and confirms both that you meet the 55% threshold and that your condition will likely not improve below this level.
7. Combined Mental/Behavioral and Physical Impairments
You qualify when a combination of mental or behavioral impairments (not including brain injury) and physical impairments together total 55% or more whole-body impairment. Medical professionals calculate mental/behavioral impairments using specific AMA guidelines (6th edition) and combine them with physical impairments using standardized tables. The same timing rules apply as for physical impairments alone—you must wait two years or receive an early medical determination.
8. Severe Mental or Behavioral Disorders
You qualify when mental or behavioral disorders cause marked impairment in three or more areas of daily functioning, or extreme impairment in one or more areas, making useful functioning impossible. Medical professionals assess these impairments using AMA guidelines (4th edition). You must wait two years after the accident unless a physician confirms in writing that your condition will likely not improve to a less severe level.
What Is the Average Payout for Car Accident Cases in Canada?
No reliable “average” payout exists for car accident cases in Canada because each claim depends on unique circumstances, injury severity, and individual factors. Canadian law relies on common law principles and comparable case precedents rather than standardized settlement charts.
Compensation assessment requires the injured person to reach maximum medical recovery, meaning doctors confirm their condition has stabilized and the long-term prognosis is clear. Only then can proper evaluation occur with supporting expert evidence.
The process involves:
- Medical experts providing opinions on long-term injury impact
- Occupational therapists assessing functional limitations and care needs
- Actuaries calculating the present value of economic losses
- Life care planners quantifying future care requirements
- Vocational experts analyzing employment capacity
Without comprehensive expert evidence, any compensation estimate represents mere speculation. The complexity of building proper evidence explains why experienced legal representation is essential for serious injury cases.
Factors influencing compensation include:
- Severity and permanence of injuries
- Age and pre-accident health status
- Occupation and earning capacity
- Family circumstances and dependents
- Quality and strength of expert evidence
- Degree of fault attributed to each party
Rather than focusing on averages, families should understand that proper legal representation ensures all compensation categories are identified, documented, and pursued to the fullest extent under Ontario law.
I was referred to Lalande Lawyers by a friend who had previously worked in a professional capacity with Mr. Lalande. He came highly recommended. It took me about a year to reach out since I was so overwwhelmed emotionally after my loss. I am so happy that I did. With 2 young children, I don’t know what I would have done without his help. Thank you from the bottom of my heart – Gayle.
If You Are Unsure About Your Compensation Rights, Lalande Personal Injury Lawyers Are Ready to Guide You
If you’ve suffered life-changing injuries in a car accident, understanding your rights and the full scope of available compensation is essential for your recovery and your family’s future. The complexity of building a strong case with proper medical, vocational, and actuarial evidence requires experienced legal guidance from lawyers who understand Ontario’s personal injury system.
Don’t wait to protect your rights. The legal process involves strict deadlines, and early action helps preserve crucial evidence and secure proper medical documentation. Call Ontario at 905-333-8888 or alternatively, fill out a confidential contact form, and we would be happy to explain your rights to you without cost or obligation.
Article FAQs
[faqs]


