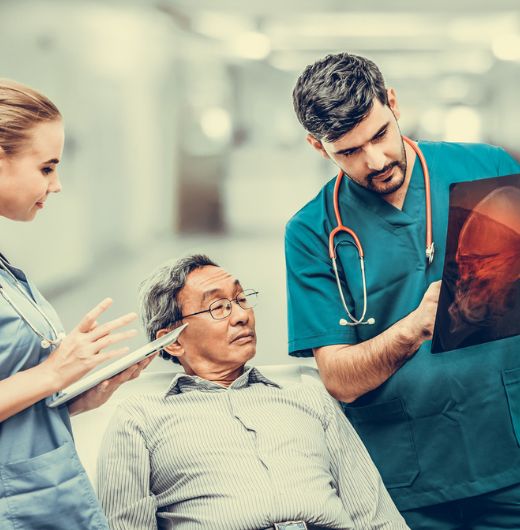
Hamilton Brain Injury Lawyers – Serving Brain Injury Victims throughout Ontario since 2003. No Fees Unless we Win.
Free Consultations Provincewide. Call 905-333-8888 or Send us a Message Today.
Don’t Let a Brain Injury Define Your Loved Ones’ Future. The Hamilton Brain Injury Lawyers at Lalande Personal Injury Lawyers Will Fight Tirelessly to Obtain the Compensation Your Loved One Deserves. Trust Us to Be Your Voice for Justice.
Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) are among the most devastating and life-altering events that a person or their loved ones can experience. The physical, emotional, and financial toll of a TBI can be overwhelming, leaving families struggling to cope with the aftermath. If you or someone you love has suffered a brain injury due to the misconduct or negligence of another party, it is crucial to understand your legal rights and the options available to you.
A traumatic brain injury can fundamentally change the course of an individual’s life, affecting their ability to work, maintain relationships, and engage in the activities they once enjoyed. The impact of a TBI extends far beyond the injured person, profoundly affecting the lives of their spouse, children, and other family members.
Spouses may find themselves taking on new roles as caregivers while also dealing with the emotional distress of seeing their loved one’s personality and abilities altered by the injury. Children may struggle to understand the changes in their parents. They may require additional support to cope with the emotional and practical challenges of having a family member with a TBI.
The financial implications of a brain injury can be equally devastating, with mounting medical bills, lost wages, and the ongoing costs of rehabilitation and assistive devices placing a tremendous strain on families already coping with the emotional impact of the injury.
The road to recovery after a TBI can be long and challenging, but you don’t have to face it alone. If someone else’s carelessness caused your injury, you have the right to seek the financial compensation you deserve. Our skilled Hamilton brain injury lawyers will fight tirelessly to ensure you receive the resources you need to cover lost wages, medical expenses, and ongoing rehabilitation and care costs. We will also seek compensation for your pain and suffering, acknowledging the emotional and psychological toll that a TBI can take on you and your loved ones.
If you or a loved one has suffered a brain injury due to someone else’s negligence, we invite you to read on and learn more about how we can help you on your path to recovery.
Matt Lalande is a leading Hamilton brain injury lawyer dedicated to securing the compensation you deserve. Since 2003, we have recovered over $65 million for injured victims. Call us today at (905) 333-8888 or fill in a contact form to learn how we can assist you.
What is a Traumatic Brain Injury?
Severe traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) are life-altering events that can have devastating consequences for both the injured individual and their loved ones. These injuries occur when a significant external force causes substantial damage to the brain, often resulting from high-impact incidents such as serious car accidents, falls from heights, or acts of violence.
The effects of a severe TBI can be immediate and catastrophic, setting the stage for a challenging and uncertain future. Upon impact, the individual may lose consciousness, experience seizures, or even fall into a coma. In the aftermath of the injury, they may face a range of physical, cognitive, and emotional impairments that can profoundly affect every aspect of their life.
Physically, a severe TBI can cause paralysis, loss of sensory function, and difficulties with balance and coordination. The injured person may require extensive medical treatment, surgeries, and long-term rehabilitation to regain even a portion of their former abilities. Sometimes, they may need lifelong assistance with daily activities and personal care.
Cognitively, severe TBIs can lead to significant memory loss, difficulty processing information, impaired judgment, and trouble with communication. These challenges can make it difficult for the individual to return to work, maintain relationships, and engage in the activities they once enjoyed. They may need ongoing therapy and support to adapt to their new limitations and relearn essential skills.
Emotionally, the impact of a severe TBI can be equally profound. The injured person may experience drastic personality changes, increased irritability, depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These emotional challenges can strain relationships with family and friends, leading to feelings of isolation and helplessness.
The road to recovery after a severe TBI is often long, uncertain, and filled with obstacles. The injured person and their loved ones may face mounting medical bills, loss of income, and the need for extensive support services. The financial burden can be overwhelming, compounding the emotional stress of the situation.
It is crucial for individuals who have suffered a severe TBI due to someone else’s negligence to seek the guidance of experienced legal professionals. A skilled brain injury lawyer can help them navigate the complex legal process, secure the compensation they deserve, and access the resources they need to rebuild their lives in the wake of this devastating injury.
Common Causes of Traumatic Brain Injuries
Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) can have life-altering consequences, affecting an individual’s cognitive abilities, physical functioning, and emotional well-being. Our Hamilton Brain Injury Lawyers understand the importance of educating family members about the common causes and risk factors associated with severe brain trauma. What are the most common causes of traumatic brain injuries that we see?
In our opinion, car accidents are a leading cause of traumatic brain injuries, with certain types of collisions posing a higher risk for severe brain trauma. Two of the most dangerous types of crashes are:
T-bone Accidents: Also known as side-impact collisions, these accidents occur when the front of one vehicle strikes the side of another, forming a “T” shape. T-bone accidents often happen at intersections when one driver fails to yield the right of way or runs a red light. The lateral force of the impact can cause the occupant’s head to violently strike the window or side pillar, leading to skull fractures, intracranial hemorrhage, and diffuse axonal injury. Even with side-impact airbags, the brain can still suffer significant trauma due to the sudden acceleration and deceleration forces.
Head-on Collisions: These frontal impact crashes occur when two vehicles collide directly, front-to-front. Head-on collisions are often the result of a driver veering into oncoming traffic due to distraction, fatigue, or impairment. The immense force generated by the combined speed of both vehicles can cause severe whiplash, where the head is rapidly propelled forward and then back, leading to brain injury. Airbags and seatbelts can help mitigate the impact, but the brain can still be subjected to dangerous rotational forces, causing shearing of neural connections and widespread damage.
In both t-bone accidents and head-on collisions, the brain is particularly vulnerable to injury due to its soft, gelatinous nature. The sudden change in velocity and direction can cause the brain to move within the skull, leading to bruising, bleeding, and tearing of delicate neural tissue. These traumatic injuries can result in a range of cognitive, physical, and emotional impairments that may require extensive medical treatment and rehabilitation.
Motorcycle Accidents: Motorcycle accidents are a leading cause of severe traumatic brain injuries due to the lack of protective structure compared to cars or trucks. While wearing a DOT-approved helmet is crucial and can significantly reduce the risk of head injury, studies show that the forces involved in a high-speed motorcycle crash can still cause traumatic brain injury, even with proper helmet use. In a severe collision, the rider may be thrown from the vehicle, causing their head to strike the pavement or other objects with tremendous force, resulting in skull fractures, intracranial hemorrhage, and diffuse axonal injury.
The severity of the injuries can vary depending on factors such as speed, angle of impact, and presence of hazards. In the event of a severe motorcycle accident caused by another party’s negligence, it is essential to consult with an experienced Hamilton Brain Injury Lawyer to protect your rights and ensure proper compensation for your injuries and ongoing medical needs.
Bicycle Accidents: Bicycle accidents can result in severe traumatic brain injuries, even when riders wear helmets. In high-speed collisions or motor vehicle accidents, the impact force can cause the brain to move within the skull, leading to bruising, bleeding, and tearing of neural tissue. Cyclists can also suffer from diffuse axonal injury, where the brain’s long connecting fibres are torn due to sudden acceleration and deceleration. While wearing a helmet is essential and can help reduce the risk of skull fractures and other head injuries, it may not always prevent traumatic brain injuries in serious accidents.
Suppose you or a loved one was involved in a severe bicycle accident caused by another party’s negligence. In that case, consulting with a knowledgeable Hamilton Brain Injury Lawyer is crucial to protect your rights and secure the compensation you deserve for your injuries and ongoing medical needs.
Pedestrian Accidents: Pedestrian accidents can lead to devastating traumatic brain injuries, as individuals are entirely unprotected when struck by a moving vehicle. The force of impact can cause the pedestrian’s head to violently strike the car, the ground, or nearby objects, resulting in severe head trauma. Common injuries include skull fractures, intracranial hemorrhage, and contusions.
The brain can also suffer from diffuse axonal injury, where the brain’s long connecting fibres are torn due to the sudden change in velocity and direction. The severity of the injury depends on factors such as the speed of the vehicle, the angle of impact, and the pedestrian’s age and overall health. Suppose you or a loved one has suffered a traumatic brain injury as a result of a pedestrian accident caused by another party’s negligence. In that case, it is essential to seek the guidance of an experienced Hamilton Brain Injury Lawyer to protect your rights and secure the compensation you deserve for your injuries and ongoing medical needs.
Commonly Diagnosed Traumatic Brain Injuries
Skull fractures – There are four common types of skull fractures:
- Linear skull fractures – Linear skull fractures are cracks or breaks in the skull. The concern when this happens is that the underlying force that created the fracture might have caused damage to the brain itself. Fractures to the base of the skull can be very problematic because they may cause damage to arteries, nerves and other structures. If a fracture reaches down to the sinuses, this may cause cerebrospinal fluid to leak from the nose and ears, and intervention may be required to insert a lumbar drain.
- Depressed skull fractures – These fractures happen when a part of the bone presses on or into the brain itself, often requiring surgical intervention. The specific damage caused will depend on the region where this fracture happens, as well as its interaction/coexistence with any diffuse brain injuries.
- Diastatic skull fractures – These are fractures that occur along the suture lines in the skull. The sutures are the areas between the bones in the head that fuse when we are children.
- Basilar skull fracture – This involves a break in the bone at the base of the skull and is usually a severe injury. These victims tend to require close observation in the hospital.
Intracranial hematomas (ICH) – When a blood vessel in the brain is ruptured, bleeding starts and the blood naturally clot. Sometimes, these hematomas are very small. When a hematoma is large, it might compress the brain. Symptoms will depend on the location of the hematoma; hematomas are named for their area.
A hematoma that forms between the skull and the dura (the tough outermost membrane enveloping the brain and spinal cord) is called an epidural hematoma. When the hematoma forms between the brain and the dura, it is called a subdural hematoma. When the hematoma forms deep inside the brain, it is named an intracerebral hematoma. Under fortunate circumstances, the body will reabsorb the hematoma. Large clots (hematomas) are periodically removed by surgery.
Some types of intracranial hematomas are:
- Epidural hematoma – It is a collection of blood in the potential space between the dura mater’s outer layer and the skull’s inner table. EHs happen in approximately 10% of traumatic brain injuries (TBI) requiring hospitalization. Most traumatic EHs occur as a result of head injury due to motor vehicle collisions, physical assaults, or accidental slips and falls.
- Subdural hematoma – This occurs when a blood clot forms outside the brain, underneath the skull and the dura. This can form from a tear in the veins from the brain to the dura or from a cut on the brain itself.
- Contusion or intracerebral hematoma – This more localized brain injury can be compared to a bruise. A forceful blow to the head usually causes it.
Diffuse axonal injury (DAI): Axons, which compose what is also known as the brain’s white matter, connect nerve cells throughout the brain. The nerve axons are torn and damaged when the brain reverberates (quickly moving back and forth inside the skull). During a car accident or when a pedestrian is hit by a car, for example, rapid rotation or deceleration of the brain can cause stretching of these nerve cells on a cellular level. The brain’s standard transmission of signals (information) is disrupted, dramatically impacting the person’s alertness and wakefulness.
Ischemia: Another diffuse injury happens when certain brain parts are cut off from an adequate blood supply. A marked decrease in blood supply is especially perilous for a brain injury victim because the brain becomes extremely sensitive with even the smallest decreases in blood supply after a traumatic injury. Changes in blood pressure during the first week post-head injury can have adverse effects.
Second Impact Syndrome (SIS): This causes the brain to swell catastrophically. SIS is not strictly speaking a type of injury, but rather an extreme response of the brain to a second blow to the head/brain (even a very mild blow) after a first impact already changed the brain’s functioning and left it in a vulnerable state.
This second impact can happen within seconds of the first or up to a few days later. A second blow to the head during concussion triggers a series of metabolic events that might start within 15 seconds. One of the ramifications is a massive increase in blood flow due to a loss of autoregulation of the brain’s blood vessels. Considerable increases in intracranial pressure follow, which might cause cerebellar herniation (the brain is squeezed past structures within the skull), which is often fatal.

Experience Matters
A few of our recent result are noted below. Past results are not necessarily indicative of future results and litigation outcomes will vary according to the facts of individual cases. The information below are examples of Matt Lalande’s cases that he has settled or tried to verdict over his career and is for informational purposes only.
View More Case ResultsFor a middle aged woman who suffered a serious head injury in a T-Bone accident.
For a young amputee victim who lost a leg and and an arm.
For a trucker who suffered serious 3rd degree burns in a california trucking accident.
How are Brain Injuries Diagnosed?
Seeking medical attention is the first thing that should occur after someone suffers a traumatic brain injury. Proving that your brain injury is related to the accident caused by the negligent party is essential for your case. Medical treatment should begin immediately after receiving a diagnosis from a physician.
A doctor may diagnose a brain injury using several methods. Your physician may use one or all of the following procedures: brain imaging testing, interviewing the patient, and the Glasgow coma scale.
Brain imaging is used in medical research and neurocognitive analysis. Two primary tools a doctor can use to diagnose a traumatic brain injury are an MRI and a CT scan. MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging, and CT stands for computed tomography.
Doctors use these tests and X-rays to examine the brain’s physical condition. They typically search for bleeding, swelling, or bruising. An MRI photographs the brain, and physicians use these images to assess the recovery stages that occur after a traumatic brain injury.
A physician may also interview a patient who suffered a traumatic brain injury. As the doctor questions the patient, the doctor will test the patient’s speech, memory, and cognitive skills. This is often one of the initial methods a physician will use to determine the condition of a patient who suffered a mild traumatic brain injury.
The Glasgow coma scale is a more complex test of a patient’s physical and mental condition that involves having the patient move their limbs, follow specific instructions, and speak. A doctor may test a patient’s hand-eye coordination or ask the patient to follow the doctor’s finger with his or her eyes.
After performing a series of tests, a physician may diagnose a traumatic brain injury as a concussion. The treatment plan for a concussion will be different if the doctor diagnoses a traumatic brain injury as a hematoma or a skull fracture.
A Hamilton brain injury lawyer will help you collect the medical records and reports you need to help support your case.
Brain Injury Symptoms
After a severe accident, CT head and MRI scans are typically used to measure changes in TBI’s anatomical or physiological parameters. These include hemorrhage, edema, vascular injury, and intracranial pressure. There are different kinds of brain injuries – with the two most common being traumatic and acquired. A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is caused by an external force, such as a hard impact or hit to the head. The impact causes the brain to move inside the skull, damaging the brain. The Mayo Clinic tells us that with a TBI, a person may experience the following symptoms:
- Loss of consciousness
- Confusion and disorientation
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Fatigue or drowsiness
- Difficulty sleeping
- Sleeping more than usual
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Word-finding problems
- Concentration difficulties
- Blurred vision and ringing in the ears
- Sensitivity to light or sound
- Memory or concentration problems
- Mood changes or mood swings
- Feeling depressed or anxious
- Agitation, or unusual behaviour
- Change in eating habits
- Persistent crying
- Unusual or easy irritability
- Changes in sleep habits
- Sad or depressed mood
- Loss of interest in favourite toys or activities
- Attention Deficit
- Impaired Language Skills
- Loss of Understanding
- Loss of Reading Skills
- Loss of Writing Skills
- Impaired Learning
- Impaired Problem Solving
- Lack of Judgment
- Impaired Memory
- Inappropriate Behavior
- Loss of Empathy
- Lack of Self-Awareness
- Irritability
- Anger
- Lack of Emotional Control
- Depression
- Mood Swings
- Loss of Drive
- Restlessness
- Frustration
- Selfishness
- Sluggishness
Traumatic Brain Injuries: Long-Term Consequences
Individuals who have suffered a severe traumatic brain injury may experience a wide range of symptoms that can significantly impact their daily lives. As a knowledgeable Hamilton Brain Injury Lawyer, it is essential to understand these symptoms to better advocate for clients and ensure they receive the support they need.
Some of the most common symptoms associated with a severe brain injury include:
- Cognitive impairments: Difficulties with memory, attention, concentration, and executive functions such as planning, organizing, and problem-solving.
- Physical symptoms: Headaches, dizziness, fatigue, weakness, sensory changes, and problems with balance and coordination.
- Communication difficulties: Challenges with speaking, writing, or understanding language, as well as difficulty expressing thoughts and emotions.
- Emotional and behavioural changes: Depression, anxiety, irritability, aggression, impulsivity, and mood swings.
- Sleep disturbances: Insomnia, excessive sleepiness, or changes in sleep patterns.
- Seizures: Development of post-traumatic epilepsy, which can occur weeks, months, or even years after the initial injury
- Sensory problems: Changes in vision, hearing, taste, smell, or touch sensitivity.
- Motor impairments: Weakness, paralysis, or difficulty with fine motor skills and coordination.
- Bowel and Bladder Incontinence: Severe brain injuries can lead to significant complications, including bowel and bladder incontinence, which profoundly impacts the quality of life and requires specialized care and management.
- Ambulation and Balance Problems: Severe brain injuries can result in difficulties with walking and ambulation, often requiring extensive rehabilitation and the use of assistive devices to help regain mobility and independence.
Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may persist for extended periods, significantly impacting an individual’s quality of life. It is crucial for family members to be aware of these potential symptoms and to seek the guidance of an experienced Hamilton Brain Injury Lawyer to ensure their loved one receives the necessary medical care, rehabilitation, and support services to manage their condition effectively.
Moreover, the long-term management of these symptoms can place a substantial financial burden on the injured individual and their family. A skilled brain injury lawyer can help clients pursue the compensation they deserve to cover the costs of ongoing medical treatment, therapy, and other necessary support services.
The Psychological Impact of a Brain Injury
Following a severe brain injury, individuals may experience a wide range of cognitive, emotional, and behavioural changes that can be both distressing and disorienting. Memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and impaired decision-making abilities are common, often leading to intense feelings of frustration, anger, and a loss of self-identity. These cognitive challenges can make it difficult for individuals to perform once-simple tasks or engage in previously enjoyable activities, further contributing to helplessness and despair.
The emotional toll of a severe brain injury cannot be overstated. Depression is one of the most common mental health conditions experienced by brain injury survivors, characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in daily activities. Anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), are also common as individuals grapple with the uncertainty of their future and the traumatic nature of their injury.
In addition to depression and anxiety, brain injury survivors may experience significant mood swings, irritability, and emotional lability. These symptoms can manifest as sudden outbursts of anger, uncontrollable crying, or inappropriate laughter, further complicating social interactions and straining relationships with loved ones. The inability to regulate emotions can be confusing and distressing for the individual and their family members, leading to feelings of isolation and disconnection.
The brain injury victim may also experience changes in personality and behaviour. Some may exhibit impulsivity, disinhibition, or aggression, while others may become more withdrawn and apathetic. These changes can be particularly challenging for family members and friends to navigate as they attempt to reconcile the person they once knew with the individual now before them.
It’s crucial to recognize that the mental health consequences of a severe brain injury are not limited to the survivor alone. Family members and caregivers often experience significant stress, burnout, and emotional turmoil as they adapt to their new roles and responsibilities. The demands of providing care, coupled with the grief and sense of loss that often accompany a loved one’s injury, can take a substantial toll on the mental health of those closest to the survivor.
Addressing the psychological impact of a severe brain injury requires a comprehensive approach to treatment and support. Access to mental health professionals, such as psychiatrists, psychologists, and counsellors, is essential for helping individuals and their families cope with the complex array of emotions and challenges they face. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness-based interventions, and support groups can be particularly effective in helping individuals develop adaptive coping strategies and build resilience in the face of their new reality.
Furthermore, it’s essential to recognize that the psychological recovery process following a severe brain injury is often ongoing and may require long-term support. As individuals navigate the various stages of recovery and adapt to their new reality, their mental health needs may evolve, necessitating a flexible and individualized approach to care. Not only can recovery take a long time, but continuously consulting these healthcare professionals can become financially draining.
Mental health comes with much stigma, and the symptoms can’t always be as quickly seen. Therefore, you may experience doubt from the insurance company. This is where an experienced Hamilton brain injury lawyer can help prove these effects are present and demonstrate your need for specialized and intensive treatment.
If you are ever in need of a personal injury lawyer we would highly recommend Matt Lalande. His team Lindsay, and Heather helped support us and keep us up to date and feeling calm and listened to everything we had to say, while Matt worked hard for us for both an AB and Tort claim. When you are going through such a complex and lengthy process you want to make sure you are partnered with the best and most knowledgeable in the industry, and Matt, Lindsay and Heather are just that. Even if you aren’t in Hamilton, I recommend Matt because he has resources and support teams all over and will make sure you have everything you need.
Medical Collaboration is Crucial in Brain Injury Rehabilitation
Recovering from a brain injury is a complex and challenging process that requires a coordinated, multidisciplinary approach to ensure the best possible outcomes. It’s essential to understand that rehabilitation is not a one-size-fits-all solution; instead, it involves a team of medical professionals, therapists, and specialists working together to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your unique needs and symptoms.
Recovery often begins with acute care, focusing on stabilizing your condition and preventing further complications. From there, you may transition to inpatient rehabilitation, where you’ll work with a team of specialists to regain lost skills and adapt to any lingering impairments. This rehabilitation phase typically involves a combination of physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and cognitive therapy.
- Physical therapy: is crucial for addressing any physical limitations or disabilities resulting from your brain injury. Your physical therapist will work with you to improve your strength, balance, coordination, and mobility, helping you regain as much function as possible. On the other hand, occupational therapy focuses on developing strategies to perform daily living activities, such as dressing, bathing, and eating, as independently as possible.
- Speech therapy: is another critical component of brain injury rehabilitation, as it helps address any communication or swallowing difficulties you may experience. Your speech therapist will work with you to improve your ability to express yourself verbally and non-verbally and develop strategies to overcome any language processing challenges.
- Cognitive therapy: is essential for addressing the cognitive impairments that often accompany brain injuries, such as memory loss, attention deficits, and problem-solving difficulties. Your cognitive therapist will work with you to develop compensatory strategies and techniques to help you manage these challenges and improve your overall mental functioning.
- Attendant care and rehabilitation therapy: You may require assistance with your day-to-day activities or re-establishing positive everyday routines and transportation on a supervised basis. Rehabilitation therapy can also help suffering individuals relearn skills such as walking, list-making, communicating or self-care. Rehabilitation therapy for a brain-injured individual can include different kinds of therapy for cognitive difficulties. These treatments may be needed only briefly after the injury, occasionally throughout a person’s life, or permanently, depending on the injury.
- Psychotherapy: You or your loved one may require ongoing funding for group support, education or long-term support. Not surprisingly, the consequences of a head injury can also affect the individual’s family members as well. It’s common for family members to need and receive information for the best involvement, counselling and emotional support, as well as help with recognition of the family’s needs, adjustment and, eventually, an excellent functional outcome.
- Physical Therapy: Often overlooked within a life-care plan, physical therapy is usually a requirement for an individual who suffers a traumatic brain injury. Those with a cognitive injury may not appreciate the need for exercise and caring for their health. Personal support or rehabilitation workers are often necessary since individuals with brain injuries do not make exercise a priority, or they are unable to drive after their injury (thus, they have difficulty getting to a gym or place to exercise). Physical limitations also impact the kinds of exercises and types of exercise machines that can be used safely, which can place victims at risk of injuring themselves while exercising.
- Medication: Brain-injured individuals may require the monitored intake of drugs such as anticonvulsants, analgesics for pain, antipsychotics (for hostility, nervousness, and severe agitation), antidepressants, anti-anxiety medication, and muscle relaxants or stimulants to increase levels of responsiveness or alertness.
- Management of Sleep Dysfunction: Immediately following a traumatic brain injury, difficulty falling asleep and frequent waking are ordinary. Medication or cognitive behavioural therapy focused on sleep may be necessary if chronic sleep disturbances develop.
- Speech Therapy: Severe accidents may damage portions of the brain that are responsible for language. Often, individuals who suffer a severe brain injury can be left with stuttering and word-finding issues, making it very difficult or impossible to communicate effectively.
- Vocational Therapy: Occupational therapists are often retained on a temporary or life-long basis to assist with vocational therapy. They help find solutions to appropriate job opportunities, address workplace challenges and ergonomic requirements, and provide general everyday transportation. Occupational therapists can make a significant and positive difference in the life of someone with a brain injury.
It’s important to remember that recovery from a brain injury is a gradual process that requires patience, perseverance, and a robust support system. By working closely with your multidisciplinary rehabilitation team and advocating for your needs, you can maximize your chances of achieving your goals and leading a fulfilling life post-injury. Your Hamilton brain injury lawyer also plays a crucial role in this process, ensuring you’re connected to the best professionals and receiving the funding you need to continue treatment.
Future Care Cost: The Importance of Life Care Planning.
The cost of caring for brain-injured patients can become astronomical. What becomes essential about the cost, however, is that the quality of care for an individual, and thus the quality of life that person can experience after the traumatic brain injury, depends on available financial resources. You must speak to a Hamilton brain injury lawyer who can retain a qualified life care planner to ensure that proper estimation of care costs required over your loved one’s life is evaluated correctly.
Our experienced brain injury lawyers work with some of Ontario’s best life care planners to ensure your loved one receives the highest care and support throughout their recovery and rehabilitation process. Life care planners are experts in assessing the long-term needs of individuals with severe brain injuries and creating comprehensive plans that outline the medical care, therapies, equipment, and services required to maximize their quality of life.
By collaborating with these skilled professionals, our lawyers can help you understand the full extent of your family member’s future needs and pursue the compensation necessary to cover these costs. This approach ensures that your loved one has access to the best possible care and that your family has the financial resources to provide that care, both now and in the future.
With our team of brain injury lawyers and our network of top life care planners, you can focus on supporting your loved one’s recovery while we work to secure the compensation you deserve.
Case Managers: Crucial Coordinators of Brain Injury Care
t our Hamilton brain injury law firm, we understand the critical role case managers play in the recovery and rehabilitation of individuals who have suffered severe brain injuries and have been deemed catastrophically impaired. Under the Accident Benefit Schedule, these individuals are entitled to case management services, which are essential for their recovery, rehabilitation, and day-to-day living.
Our Hamilton brain injury lawyers will typically retain a case manager, as we recognize their vital role in ensuring quality care and cost-effectiveness throughout the rehabilitation process. We work with case managers who are healthcare professionals, such as occupational therapists, rehabilitation therapists, physiatrists, or nurses trained in head trauma.
We value the expertise of our case managers, who serve as a liaison between our legal team, the client, and the healthcare providers. They advocate for the injured victim and advise us on available treatments and options. Our case managers also ensure that the rehabilitation program runs smoothly and that insurance funds are allocated appropriately and in a timely manner.
In our experience, we have found that occupational therapists well-versed in head and brain trauma make the most effective case managers. Their medical background allows them to communicate more easily with physicians and other healthcare providers regarding appointments, opinions, progress updates, treatment coordination, and recommended improvements.
Matt Lalande: Your Advocate for Brain Injury Justice in Hamilton
When you entrust your case to Lalande Personal Injury Lawyers, you can be confident that you have a team of dedicated, experienced, and successful advocates. Our firm has a proven track record of achieving exceptional client results, having recovered over $65 million in compensation for injured victims.
We have earned a reputation for excellence in the legal community, as evidenced by our numerous positive Google reviews from satisfied clients who have experienced firsthand the commitment, compassion, and expertise we bring to every case.
Our lawyers have extensive trial experience and are unafraid to handle complex, challenging cases. The insurance industry knows us as a firm with credibility, expertise, and a relentless work ethic. This recognition often leads to more favourable settlements for our clients, as insurers understand we have the necessary skills and resources to succeed in court.
To build the most robust case, we collaborate with a network of top experts and life care planners who provide invaluable insights and testimony to support your claim. Working with these respected professionals ensures that every aspect of your case is thoroughly investigated and persuasively presented.
At Lalande Personal Injury Lawyers, we understand the profound impact that a severe brain injury can have on your life and the lives of your loved ones. That is why we are dedicated to providing exceptional legal representation and unwavering support and guidance throughout the legal process.
With our team in your corner, you can focus on your recovery and your family, knowing your case is in the hands of skilled, compassionate professionals fighting tirelessly to secure the compensation you deserve.
If you or a Loved one has Suffered a Serious Brain Injury, we can help.
Matt Lalande is a Hamilton brain injury lawyer who has represented victims across Ontario since 2003. We have represented victims with personal injury cases involving severe, catastrophic head trauma and recovered millions of dollars in compensation for injured parties and families of injured loved ones. Over the years, we have gained substantial knowledge and experience working with victims of severe injuries such as wrongful death, catastrophic injuries to the brain, and spinal cord injury, as well as long-term disability.
At Lalande Personal Injury Lawyers, we take pride in being trusted Hamilton personal injury lawyers since 2003. Over the years, we’ve helped our clients recover more than $45 Million in settlements and verdicts in personal injury, disability, and employment law cases. Whether you’re dealing with a life-changing injury, a denied disability claim, wrongful death, a hurt child or employment termination, we are here to provide compassionate and experienced legal representation. If you believe you have a case, call us today—we’re ready to help you secure the compensation you deserve.
Call Lalande Personal Injury Lawyers today, no matter where you are in Ontario at 905-333-8888 for your free consultation. Alternatively, you can contact us online, confidentially, by filling out a contact form.
Brain Injury Law FAQ
A catastrophic brain injury is a severe injury that results in significant, long-term damage to the brain, often leading to permanent cognitive, physical, and emotional impairments that affect an individual’s ability to function independently.
The most common causes of traumatic brain injuries include falls, motor vehicle accidents, sports-related injuries, assaults, and struck-by incidents.
Signs and symptoms of a traumatic brain injury may include loss of consciousness, confusion, headache, dizziness, nausea, fatigue, sleep disturbances, sensory problems, memory loss, concentration issues, and mood changes.
In Ontario, the general limitation period for filing a brain injury claim is two years from the date of the incident. However, there are some exceptions, so it’s essential to consult with a Hamilton brain injury lawyer as soon as possible.
When hiring a brain injury lawyer, look for experience handling similar cases, a proven track record of success, strong communication skills, and a compassionate approach. Choose a lawyer who makes you feel comfortable and confident in their ability to represent your interests.
A Hamilton brain injury lawyer can help you navigate the complex legal process, gather evidence to support your claim, negotiate with insurance companies, and fight for the compensation you deserve. They can also connect you with medical experts and other resources to aid in your recovery.
A no-win, no-fee arrangement, also known as a contingency fee agreement, means that you only pay your lawyer if they successfully recover your compensation. If your case is unsuccessful, you don’t owe any legal fees.
Many Hamilton brain injury lawyers, including Lalande Personal Injury Lawyers, offer contingency fee arrangements, which means you don’t pay any upfront costs. Instead, your lawyer receives a percentage of the settlement or award if your case is successful.
A case manager in a brain injury case helps coordinate the victim’s rehabilitation, advises the lawyer on treatment options, communicates between the lawyer, client, and healthcare professionals, and advocates for the injured victim.
A life care planner helps determine a brain injury victim’s long-term medical and financial needs, creating a comprehensive plan that accounts for future treatment, therapy, equipment, and care costs.
In Ontario, you may still be able to pursue a brain injury claim even if you were partially at fault for the accident. Ontario follows a comparative negligence system, meaning your compensation may be reduced based on your percentage of fault.
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a standardized assessment tool used to evaluate a person’s level of consciousness following a brain injury. It assesses eye-opening, verbal, and motor responses, with scores ranging from 3 to 15. Lower scores indicate more severe brain injuries.
Yes, consultations with Lalande Personal Injury Lawyers are free and without obligation. During the consultation, a Hamilton brain injury lawyer will review your case, answer your questions, and discuss your legal options.
To schedule a free consultation with a Hamilton brain injury lawyer at Lalande Personal Injury Lawyers, you can call their office at 905-333-8888, submit an online inquiry through their website, or visit their office located at 1 King Street West, Suite 1705, Hamilton, Ontario, L8P 1A4.
It depends on how serious the case is and, more importantly, the insurance limits on the person or vehicle in place that caused or contributed to your brain injury.
Despite initial hospitalization and inpatient rehabilitation services, about 50% of people with TBI will experience further decline in their daily lives or die within 5 years of their injury.
During your initial consultation, a Hamilton brain injury lawyer will review the details of your case, ask questions about the accident and your injuries, and assess your legal options. They will also discuss their experience, fees, and the next steps in the process. This consultation is also an opportunity for you to ask questions and determine if the lawyer fits your needs.
We suggest you and your family interview several lawyers and retain the lawyer with whom you have the best connection. You can begin your search by asking those around you for referrals, browsing online directories, or doing a Google search and examining various websites, noting each lawyer’s experience, areas of specialty, and reviews/testimonials.